Practical No. 10023: WBCs Count Step By Step
Title/ Aim: To perform the Total WBCs Count of a given sample.
Principle
The glacial acetic acid lyses the red cells while the gentian violet slightly stains the nuclei of the leukocytes. The blood specimen is diluted 1:20 in a WBC pipette with the diluting fluid & cells are counted under low power objective. The number of cells in undiluted blood is calculated & reported as the number of WBC/cumm of whole blood.
Requirements:
1. Microscope
2. Improved Neubauer’s chamber
3. WBC pipette
4. WBC diluting fluid
5. Capillary blood or EDTA Blood
Procedure
1. Draw blood up to 0.5 mark of W.B.C pipette.
2. Wipe excess blood outside the pipette by using cotton.
3. Draw diluting fluid up to 11 mark.
4. Mix the contents in the pipette. After 5 minutes discard, a few drops charge the counting chamber, and allow the cells to settle for 2 to 3min.
5. Adjust the chamber by using a low-power objective.
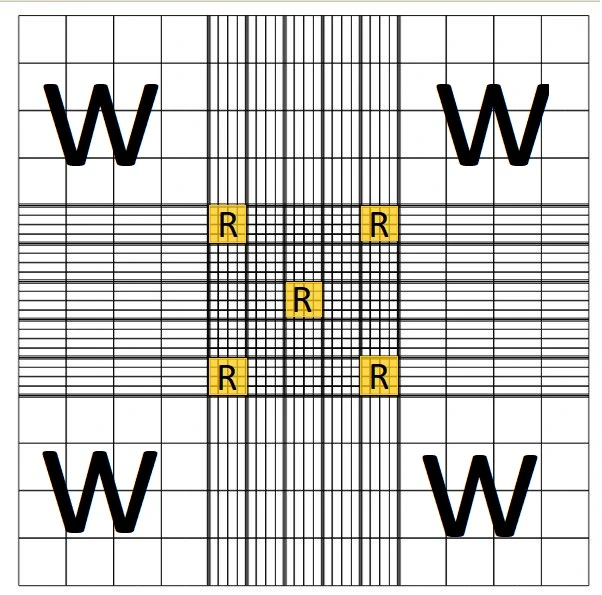
6. Count the number of cells in large four-corner squares.
7. While counting cells attached to the left and upper margin are counted and those attached to the right and lower margin are not counted.
Clinical significance
An increase in total leucocyte count of more than 10,000 is called Leukocytosis and a decrease in count of less than 4,000 is called Leucopenia.
Causes of leukocytosis: It may be physiological or pathological.
Physiological
· Age- At birth, the total leukocyte count is about 18000/cumm it drops gradually to the adult level.
· Pregnancy- At ‘full term’, the total count tends to be about 12000 to 15000 /cumm. It rises soon after delivery and then gradually returns to normal.
· High temperature
· Severe pain
· Muscular exercise
Pathological:
· It is for a transient period of infection.
· The degree of rise in leucocytes depends on 23 the type & severity of infection& response of
the body.
· The infection may be bacterial, viral, protozoal, or parasitic.
· Leukocytosis is also observed in severe hemorrhage.
· Leukemia.
Cause of leucopenia certain viral and bacterial infections lead to leucopenia.
1. Infections
· Bacterial (typhoid, paratyphoid, tuberculosis)
· Viral (hepatitis, influenza, measles)
· Protozoal (malaria)
2. Some cases of leukemia
(Subleukemic leukemia), Anemia (iron deficiency, megaloblastic, Aplastic)